Introduction
Most of us are familiar with the word insulin and have an understanding that it is linked with diabetes. However, a sound understanding of the production, storage, working, and related disorders is unclear to many. Knowing a detailed account of this significant hormone can help in the better management of diabetes and other health conditions.
The following blog covers a detailed explanation of the working, types, resistance, and myths about insulin. It also describes the link between insulin and diabetes.
What is insulin?
Insulin is a hormone synthesized inside the pancreas. Hormones are special protein molecules that perform the function of delivering chemical messages in the body. These protein entities travel in the bloodstream and stimulate other organs to perform specific actions. Specialized cells called the beta cells of pancreas produce insulin on the command of INS genes. Insulin is the chief hormone responsible for the anabolism (synthesis of complex biomolecules) inside the human body.
Insulin hormone is released in the well-fed state to increase the storage and utilization of the sugars, mainly glucose, present in the bloodstream. Glucose is highly important in the formation and proper functioning of energy in the body which is why effective regulation of glucose according to the requirements of the body is crucial. Since insulin chiefly manages that, imbalance or inadequate production of insulin leads to major disorders.
Key functions of insulin
Insulin is an important hormone of the body having the key function of regulation of blood sugar levels. Insulin is chiefly responsible for the regulation of carbohydrates, fats, and protein by increasing the uptake of glucose from the blood into the liver, fat, and skeletal muscle cells.
To gain an in-depth understanding of the function of insulin, it is important to have a brief understanding of the ways energy is produced and stored in the body. In the well-fed state of the body, an abundant amount of energy is present, so the body tends to store the energy, whereas, during fast or starvation, the body utilizes its energy reservoirs to extract energy. In layman’s terms, it can be stated that utilizable energy is present in the form of glucose, whereas stored forms are glycogen, lipids, and proteins.
Insulin is functional during the fed state and increased sugar levels in the blood stimulate its release from the beta cells of the pancreas. Many major tissues and cells including muscles, liver, and adipose tissues are labeled as insulin-dependent as they require insulin to uptake intracellular glucose for their energy requirements. Upon absorbing the excess glucose from the blood by the action of insulin, these tissues convert it into storable forms, i.e. glycogen, proteins, and lipids. During well-fed states, using insulin the body ensures that the synthesis and release of glucose by the liver is inhibited.
Link between insulin and diabetes
Diabetes is a chronic condition in which either the pancreas becomes unable to produce adequate amounts of insulin or the body is unable to utilize the already existing insulin leading to abnormally increased levels of sugar inside the blood. These increased levels when reach to various body parts can cause damage to them leading to thyroid, vision, kidney, and dental problems.
Type 1 diabetes indicates inadequate or lack of production of insulin in the body. This type of diabetes is thus treated by insulin medications. Type 2 diabetes on the other hand is due to a lack of sensitivity of cells toward already existing insulin. This type of diabetes is usually treated with exercise and healthier lifestyle changes but in some cases, insulin medication is used.
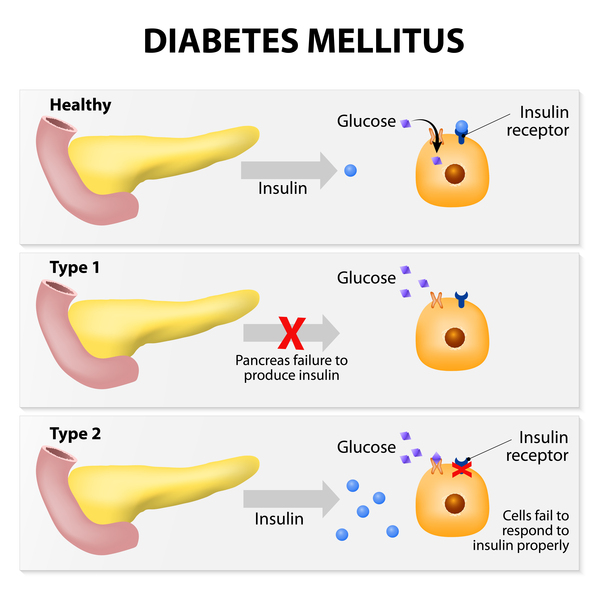
Insulin resistance
Insulin resistance is a condition in which the tissues and cells of the body stop responding optimally to insulin. As a result, muscles, adipose tissues, and the liver fail to take up the glucose from the blood. This hinders the functionality of these insulin-dependent cells and also aids in the elevation of blood glucose levels. When the Beta cells of islets of the pancreas sense the increase in blood sugar levels, they produce more and more insulin. Insulin resistance can lead to multiple disorders including diabetes, high blood pressure, obesity, high cholesterol, etc.
Insulin injections and diabetes management
Since diabetes is concerned with the inability of the body to either synthesize or utilize insulin, the administration of insulin is often used as a therapy. In most cases, insulin is administered into the body either with a needle, pump, or pen. There are various types of injectable insulin available today whose dosage and type are decided according to your condition. Since insulin is to be self-administered, the provider will educate you thoroughly about the ways you can safely and effectively take your insulin dose.
Types of Insulin
There are various types of insulin depending on their duration of action. Bolus or mealtime insulin is the type of insulin that is taken before meals as this insulin acts quickly and its action lasts for only a few hours. The other slower-acting insulin is called background or basal insulin. Basal insulin acts slower as it takes more time to reach the bloodstream, making its action last for one or two days. Bolus and basal insulin can be used separately or can be prescribed as a combination according to your condition.
Other major types include;
Rapid-acting insulin
This type of insulin starts working within five to twenty minutes and continues to function for three to five hours. It reaches its peak effectiveness after an hour or two of injection.
Short-acting insulin
It is also called regular insulin. This type of insulin starts its action in about 30 to 45 minutes which lasts only for five to eight hours. This insulin reaches its maximum effective state after two to four hours of administration.
Intermediate-acting insulin
This type of insulin starts its action about two hours after being injected and its action lasts for about 14 to 24 hours. This insulin reaches its peak between four to twelve hours.
Long-lasting insulin
Long-lasting insulin acts within an hour of injection and its effects last for about a day. The action peaks between three to fourteen hours of injection.
Ultra-long-acting insulin
Like its name, its action lasts the longest which is up to two days. This insulin reaches the bloodstream slowly by taking the time of about six hours to enter the stream.
Myths about insulin therapy
Insulin can be very useful for the treatment and management of both diabetes, especially type 1. However, a vast variety of populations around the globe are scared to use insulin therapy owing to the myths around it. Following are some myths along with actual reality written below to clear your concepts.
Insulin therapy can completely treat diabetes
Unfortunately, Insulin can still not treat diabetes and there is no cure discovered for diabetes yet. However, insulin administration can greatly help in the management of the symptoms.
Insulin therapy will limit the individual’s functionality
Getting used to the administration of insulin can be lengthy but it doesn’t hinder the normal functionality of life and such individuals can make the most of their lives by keeping their insulin levels in check.
Insulin injections are painful
Individuals having needle phobia may face trouble during insulin therapy but with modern advancements in science, most insulin pens are painless. Individuals can also opt for insulin pumps to avoid injections.
Insulin elevates the onset of severe hypoglycemia
Insulin works to utilize the elevated sugar levels in the bloodstream which can increase the risk of lowering blood glucose levels and causing hypoglycemia. However, it prevents an abrupt decrease in blood sugar levels.
Insulin therapy continues to cause weight gain
When an individual starts insulin therapy, they might notice weight gain. This weight gain is due to the body’s newness to the therapy which is not an ongoing effect.
You can inject insulin anywhere you want
The site of injection of insulin determines the rate of its absorption. The faster it is absorbed, the quicker it will drop blood glucose levels. Thus it is important to select the site of administration according to the state of your consumption.
Insulin therapy can cause addiction
Insulin cannot make one addicted as it is not an addictive drug and it is a natural substance found in the body required for its functionality.
To clear other myths surrounding insulin and insulin therapy, consult the best doctors in Pakistan using Sehat Kahani’s telemedicine mobile application. Select the diabetologist or endocrinologists of your choice and book an appointment today.
Takeaways
To summarize, insulin is an important hormone which regulates the utilization and consumption of glucose in the body. It also regulates the breakdown of fats and proteins. The pancreas is responsible for the secretion of insulin. Inadequate production or lack of response of body cells to insulin causes various disorders in the body.
There are many myths surrounding insulin, its function, and its administration. Thus it is important to generate awareness about this hormone. Individuals can administer insulin shots upon the advice of their doctors to counter insulin resistance. There are multiple varieties of insulin available for administration depending on the requirement.




